Special Populations (SPO)
Poster Session I
PI-085 - CEFEPIME PHARMACOKINETICS IN CRITICALLY ILL CHILDREN UNDERGOING CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT THERAPY (CRRT).
Wednesday, March 22, 2023
5:00 PM - 6:30 PM EDT
K. Pavia1, H. Hambrick1, K. Paice1, P. Tang1, A. Vinks1,2, J. Kaplan1, T. Mizuno1, S. Tang Girdwood1; 1Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, USA.

Kathryn Pavia, MD
Critical Care Fellow
Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center
Cincinnati, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Cefepime (FEP) is an antibiotic commonly used to treat sepsis and is renally cleared, requiring dose adjustment for continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT). A pediatric study by Stitt et al of cefepime PK/PD on CRRT used 4 young children, 3 with liver failure (1). Our study aimed to compare PK/PD of an older, diverse population to Stitt’s cohort.
Methods: Patients were included if enrolled in an ongoing IRB-approved PK/PD study on beta lactams, had at least 2 FEP doses in the ICU, and were on CRRT for at least 24h. Total FEP concentrations were measured using a validated HPLC assay. PK/PD parameters were estimated using MwPharm++ (Mediware, Czech Republic) with Bayesian estimation and a pediatric population PK model (2). 20% protein binding was assumed to calculate fT>MIC
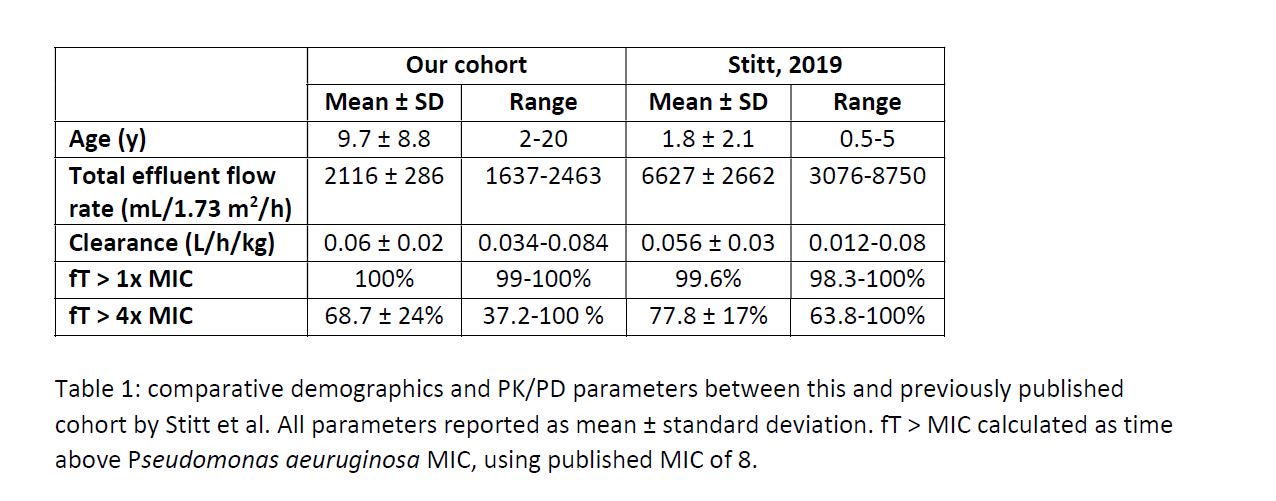
Results: Seven patients were included. CRRT indications were liver failure (n=1), renal failure (n=4), and fluid overload (n=2). PK/PD parameters were comparable to published cohort (Table 1). Using P. aeruginosa MIC FEP breakpoints, all patients had 100% fT>MIC, but only 1 had 100% fT>4xMIC
Conclusion: This is the largest pediatric study of FEP PK/PD on CRRT, with diverse ages and CRRT indications. Effluent rates were lower, but clearance and target attainment were similar to those published previously. Since few patients attain 100% t>4xMIC, model-informed precision dosing may be of benefit
Stitt G, Morris J, Schmees L, Angelo J, Akcan Arikan A. Cefepime Pharmacokinetics in Critically Ill Pediatric Patients Receiving Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(4):e02006-18. doi:10.1128/AAC.02006-18
Shoji K, Bradley JS, Reed MD, van den Anker JN, Domonoske C, Capparelli EV. Population Pharmacokinetic Assessment and Pharmacodynamic Implications of Pediatric Cefepime Dosing for Susceptible-Dose-Dependent Organisms. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016;60(4):2150-2156. doi:10.1128/AAC.02592-15
Table 1: comparative demographics and PK/PD parameters between this and previously published cohort by Stitt et al.