Oncology (ONC)
Poster Session II
PII-039 - PHARMACOKINETICS OF INTESTINAL P-GLYCOPROTEIN SUBSTRATE DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE WITH AND WITHOUT CONCOMITANT QUIZARTINIB.
Thursday, March 23, 2023
5:00 PM - 6:30 PM EDT
H. Zahir, Y. Bermudez, Y. Mostafa Kamel, N. Said, C. Hsu, M. Abutarif, M. Zheng; Daiichi Sankyo, Basking Ridge, NJ, USA.
.jpg)
Ming Zheng, PhD
Daiichi Sankyo, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Quizartinib (Q) is a receptor tyrosine kinase FLT3 inhibitor and a potential therapy for FLT3-ITD-positive AML. Q is a weak P-gp inhibitor in vitro. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of Q on the pharmacokinetics (PK) of an intestinal P-gp substrate, dabigatran etexilate (DE).
Methods: This was a phase 1, open-label, fixed-sequence, drug-drug interaction study (NCT04459585). Healthy adults received DE (150 mg, oral, period 1 [P1]) and 60 mg, oral Q + DE (150 mg, oral, period 2 [P2]). Serial blood samples were taken after DE. The primary endpoint was PK of the active moiety of DE, dabigatran (D), measured as total and free D. Endpoints included safety.
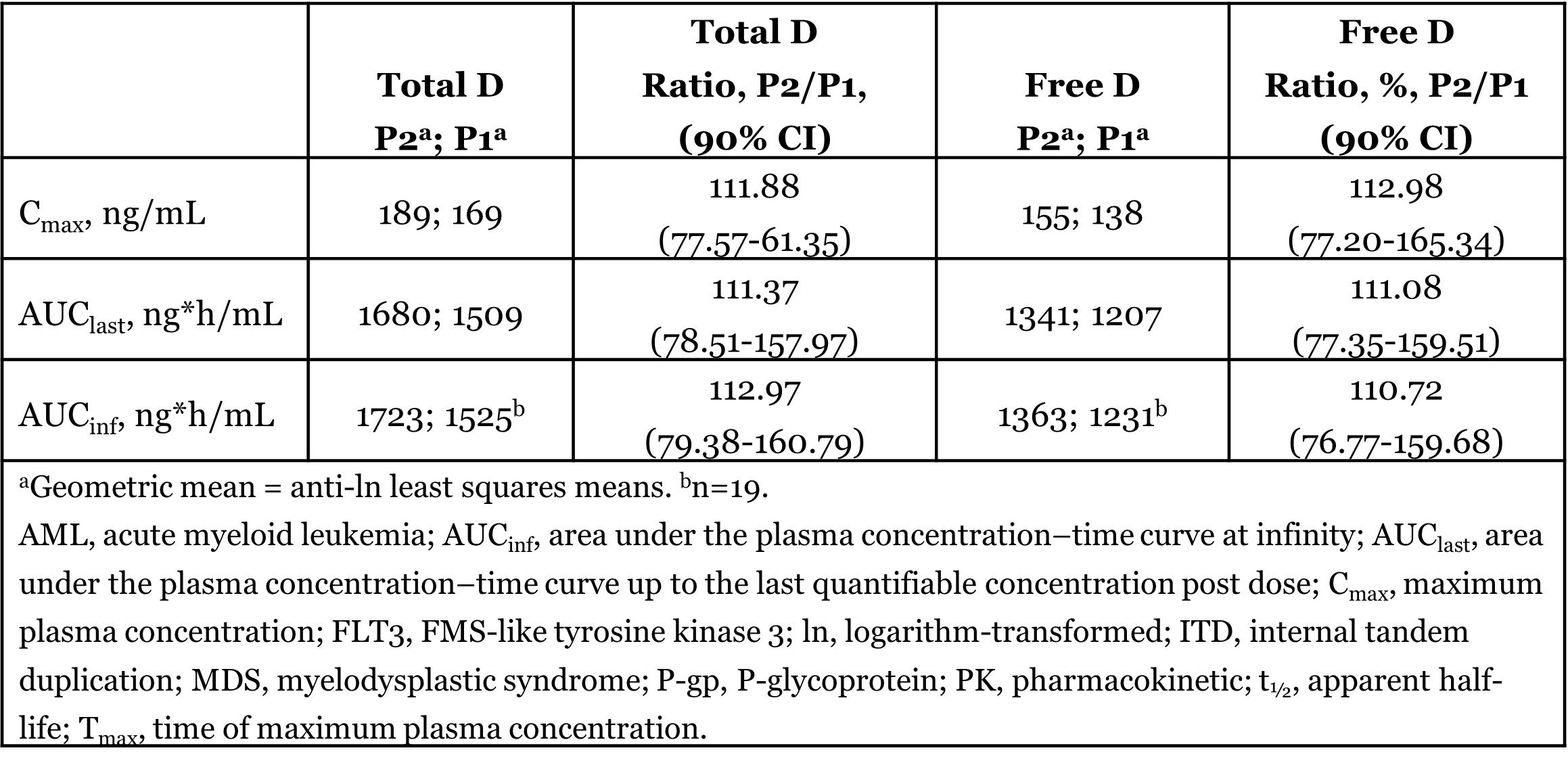
Results: Subjects were 55% (11/20) male and mostly Black (60%) with a mean (SD) age of 39 (10) years. Median Tmax for total D was 2.0 h in P2 and P1 (range, 1.5-4.0 h and 1.5-3.1 h, respectively). Q increased total and free D Cmax by approximately 12% and 13%, respectively, and increased total and free D AUCinf by approximately 13% and 11%, respectively (Table 1). Mean t½ of total D was similar for P2 (18.1±17.0 h) and P1 (15.4±4.4 h). Coadministration was well tolerated.
Conclusion: Q is a weak inhibitor of P-gp and may be coadministered with P-gp substrates.
Table 1. Statistical Comparison of Total and Free D Exposure (N=20)