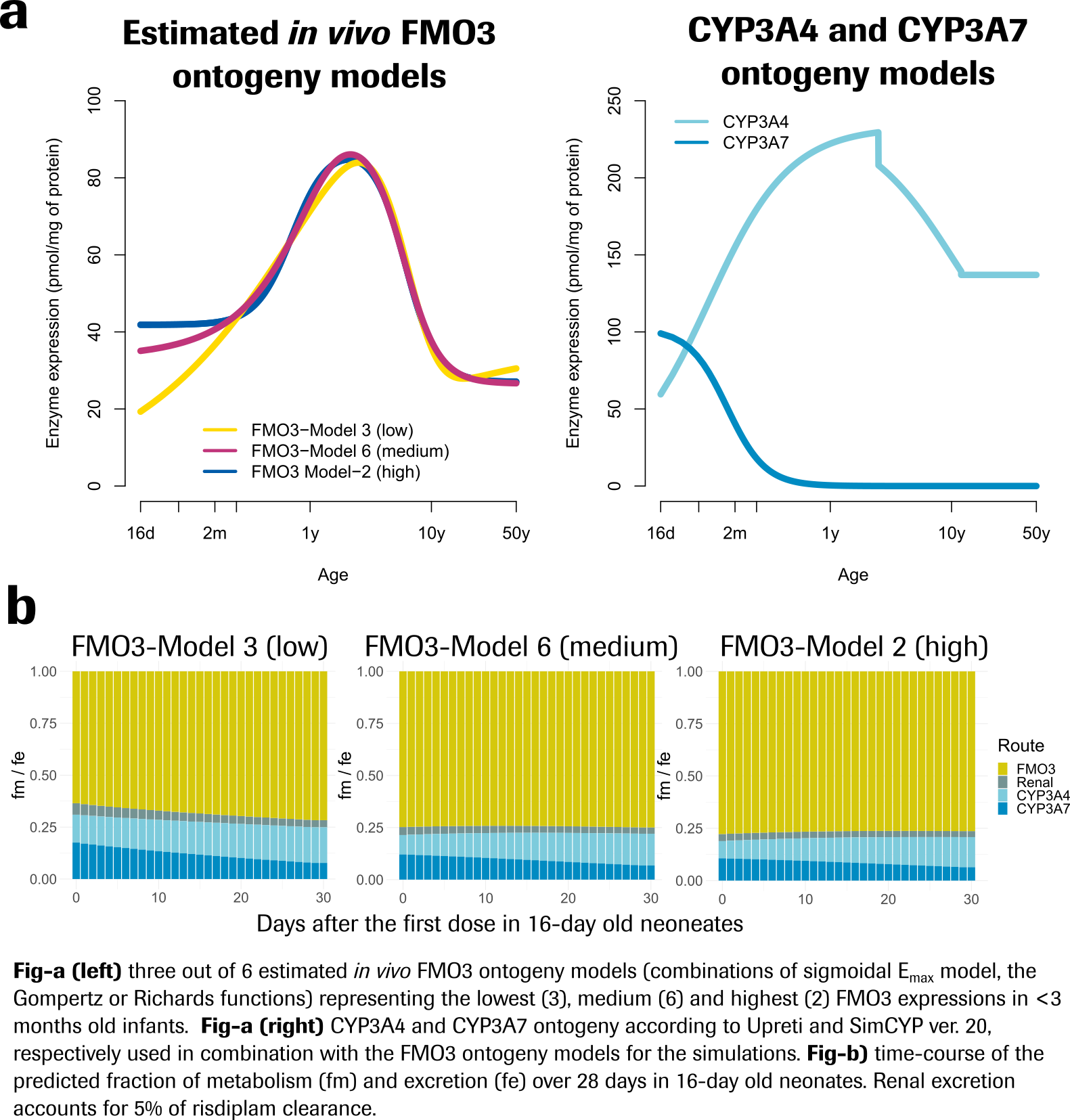Back
Background: Risdiplam (EVRYSDI) is approved for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). It is eliminated by hepatic metabolism via FMO3 (75%) and CYP3A (20%)1 in adults. The aim of this study was to evaluate adequacy of the risdiplam 0.15 mg/kg dose and CYP3A victim drug-drug interaction (DDI) risk in 16-day old neonates by mechanistic population pharmacokinetic (Mech-PPK) and physiologically-based PK (PBPK) modelling1,2.
Methods: FMO3 ontogeny was estimated using 6 different models implemented in a Mech-PPK model using >13,000 observations from 551 subjects 16 days to 61 years old. Equivalent hepatic metabolism by CYP3A4 and CYP3A7 was assumed as well as 95% inhibition of both enzymes for the DDI prediction.
Results: The 6 Mech-PPK models predicted different FMO3 ontogeny in infants < 3 months old. Three of them (Fig-a) were used to predict exposure and CYP3A DDI propensity (Fig-b) in neonates to account for the uncertainty. The simulated risdiplam AUC in 16-day old neonates (n=400), even under strong CYP3A4/7 inhibition, was comparable with PK data in older children at the approved risdiplam dose, indicating unlikely victim CYP3A4/7 DDI risk and supporting 0.15 mg/kg as the appropriate dose.
Conclusion: Mech-PPK and PBPK modelling coupled with investigation of ontogeny is a useful approach to extrapolate PK and DDI to neonates.
1. Fowler S, et al. Addressing Today's Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) Challenges in the Translation of In Vitro ADME Characteristics to Humans: A Case Study of the SMN2 mRNA Splicing Modifier Risdiplam. Drug Metab Dispos. 50(1): 65-75 (2022).
2. Cleary Y, et al. Model-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Extrapolation Strategy From Adults to Children: Risdiplam in Pediatric Patients With Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 110(6): 1547-57 (2021).
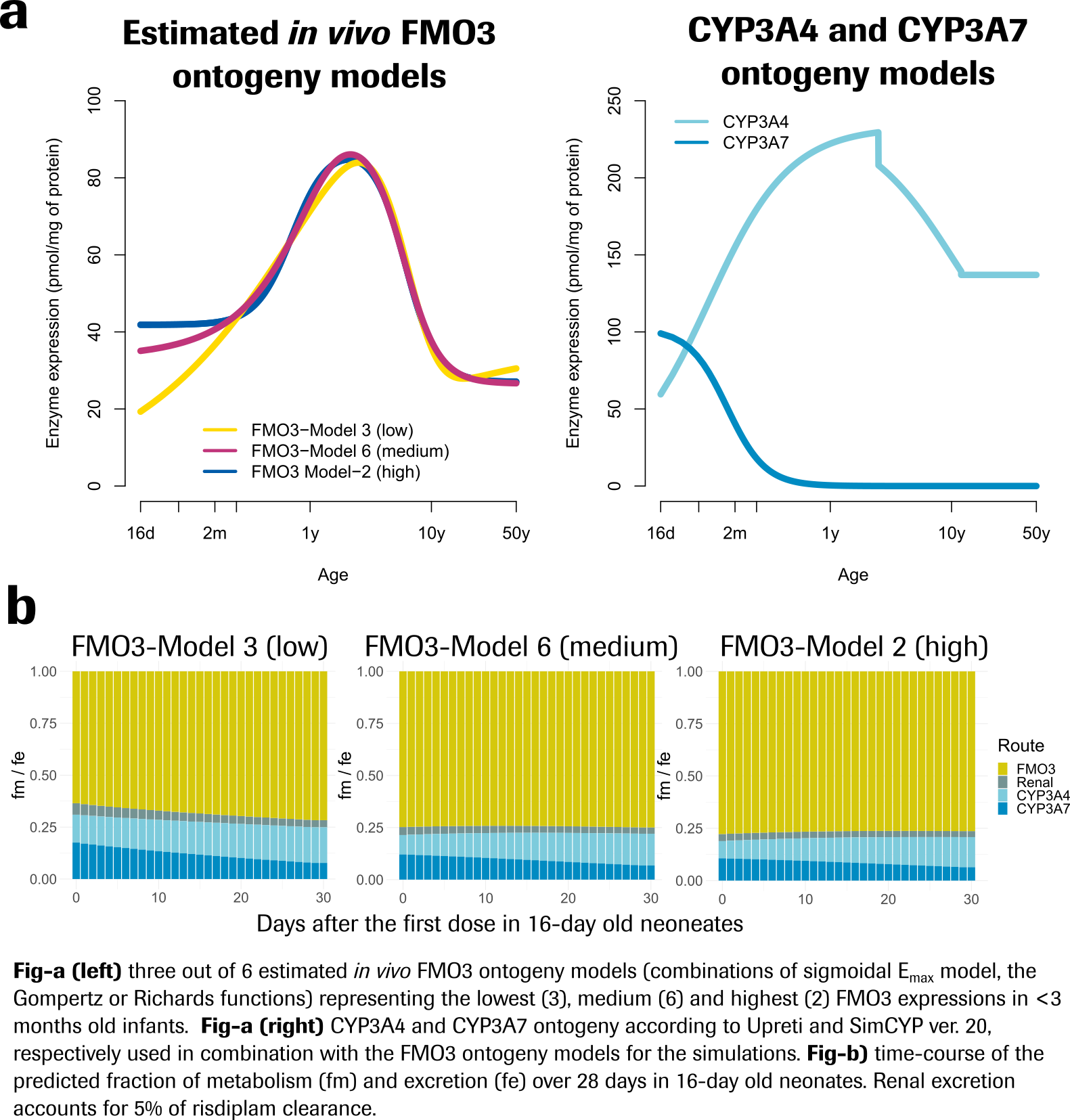
Pharmacometrics & Pharmacokinetics (PMK)
ePoster Gallery
EP-035 - MECHANISTIC POPULATION PHARMACOKINETIC MODELLING OF RISDIPLAM FOR EXTRAPOLATION OF EXPOSURE AND CYP3A DRUG-DRUG INTERACTION IN NEONATES WITH SPINAL MUSCULAR ATROPHY.
Wednesday, March 22, 2023
12:00 AM EDT
Y. Cleary1,2, H. Kletzl1, P. Grimsey3, K. Heinig1, K. Ogungbenro2, H. Silber-Baumann1, N. Frey1, L. Aarons2, A. Galetin2, M. Gertz1; 1F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland, 2University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom, 3F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Welwyn, United Kingdom.

Yumi Cleary (she/her/hers)
Senior Principal Scientist
F.Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
Basel, Basel-Stadt, Switzerland
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Risdiplam (EVRYSDI) is approved for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA). It is eliminated by hepatic metabolism via FMO3 (75%) and CYP3A (20%)1 in adults. The aim of this study was to evaluate adequacy of the risdiplam 0.15 mg/kg dose and CYP3A victim drug-drug interaction (DDI) risk in 16-day old neonates by mechanistic population pharmacokinetic (Mech-PPK) and physiologically-based PK (PBPK) modelling1,2.
Methods: FMO3 ontogeny was estimated using 6 different models implemented in a Mech-PPK model using >13,000 observations from 551 subjects 16 days to 61 years old. Equivalent hepatic metabolism by CYP3A4 and CYP3A7 was assumed as well as 95% inhibition of both enzymes for the DDI prediction.
Results: The 6 Mech-PPK models predicted different FMO3 ontogeny in infants < 3 months old. Three of them (Fig-a) were used to predict exposure and CYP3A DDI propensity (Fig-b) in neonates to account for the uncertainty. The simulated risdiplam AUC in 16-day old neonates (n=400), even under strong CYP3A4/7 inhibition, was comparable with PK data in older children at the approved risdiplam dose, indicating unlikely victim CYP3A4/7 DDI risk and supporting 0.15 mg/kg as the appropriate dose.
Conclusion: Mech-PPK and PBPK modelling coupled with investigation of ontogeny is a useful approach to extrapolate PK and DDI to neonates.
1. Fowler S, et al. Addressing Today's Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) Challenges in the Translation of In Vitro ADME Characteristics to Humans: A Case Study of the SMN2 mRNA Splicing Modifier Risdiplam. Drug Metab Dispos. 50(1): 65-75 (2022).
2. Cleary Y, et al. Model-Based Drug-Drug Interaction Extrapolation Strategy From Adults to Children: Risdiplam in Pediatric Patients With Spinal Muscular Atrophy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 110(6): 1547-57 (2021).