Infectious Diseases (INF)
Poster Session I
PI-007 - PHARMACOKINETICS OF REMDESIVIR AND ITS METABOLITES IN PARTICIPANTS WITH MODERATE AND SEVERE HEPATIC IMPAIRMENT.
Wednesday, March 22, 2023
5:00 PM - 6:30 PM EDT
S. Regan, T. Chang, M. Abdelghany, J. Llewellyn, A. Baysa, S. Davies, D. Xiao, G. Shen, S. Girish, H. Winter, R. Humeniuk; Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA, USA.

Sean Regan (he/him/his)
Clinical Pharmacologist
Gilead Sciences
Foster City, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Remdesivir (RDV) is an RNA polymerase inhibitor approved for treatment of COVID-19 [200 mg loading dose, 100 mg qd thereafter] in adult and pediatric patients, primarily metabolized by the high-capacity carboxylesterase 1 pathway (80% of metabolism), and by cathepsin A and CYP3A (10% each). The extensive hepatic contribution to RDV elimination and the prevalence of liver comorbidities in COVID-19 patients warranted a study in participants with hepatic impairment (HI).
Methods: This is a phase I, open-label study of RDV consisting of moderate and severe HI participants and healthy matched controls (HMC) based on age (±10 years), sex, and BMI (±20%). Participants received a single 100 mg IV dose of RDV and remained in the clinic for 8 days. The primary endpoint was pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters of RDV and metabolites.
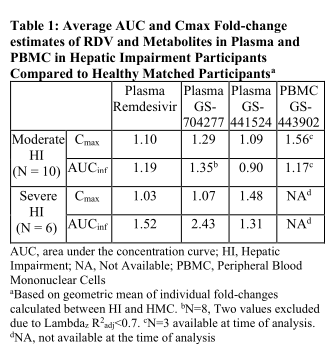
Results: Preliminary PK and safety data from 10 moderate and 6 severe HI participants and their HMC are available. The average PK fold-change for all analytes and matrices assessed in the study are presented in Table 1. No serious treatment-related adverse events and no clinically significant changes in participant lab values were reported.
Conclusion: The 1.52 RDV AUCinf fold increase is within expected ranges and justifies no dose adjustment in COVID-19 patients with impaired hepatic function.
Average AUC and Cmax Fold-change estimates of RDV and Metabolites in Plasma and PBMC in Hepatic Impairment Participants Compared to Healthy Matched Participants