Pharmacometrics & Pharmacokinetics (PMK)
Poster Session I
PI-044 - CLINICAL DRUG–DRUG INTERACTION STUDIES TO EVALUATE THE EFFECTS OF BEMPEDOIC ACID, A SMALL-MOLECULE INHIBITOR OF ATP CITRATE LYASE, ON THE PHARMACOKINETICS OF CONCOMITANT STATIN THERAPIES.
Wednesday, March 22, 2023
5:00 PM - 6:30 PM EDT
M. Emery, M. Louie, J. Hanselman, W. Sasiela, B. Amore; Esperion Therapeutics, Inc., Ann Arbor, MI, USA.

Maurice G. Emery, PharmD, PhD (he/him/his)
Consultant, Clinical Pharmacology
Esperion Therapeutics, Inc.
KULA, Hawaii, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Bempedoic acid (BA) combined with maximally tolerated statins is approved in adults with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia or atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The effects of BA on statin pharmacokinetics (PK) were studied at differing dose intensities, as BA is a weak in vitro inhibitor of organic anion transport protein 1B1.
Methods: Effects of steady-state BA 180 mg (therapeutic dose) after once daily (QD) dosing were determined on the PK of concomitant single-dose simvastatin 40 mg, rosuvastatin 40 mg, and pravastatin 80 mg and single- and multiple- dose atorvastatin 80 mg. Effects of steady-state BA 240 mg (supratherapeutic) on low-intensity statins were also studied. Natural log-transformed area under the curve (AUC) and peak concentration (Cmax) were analyzed using an analysis of variance test with treatment as a fixed effect.
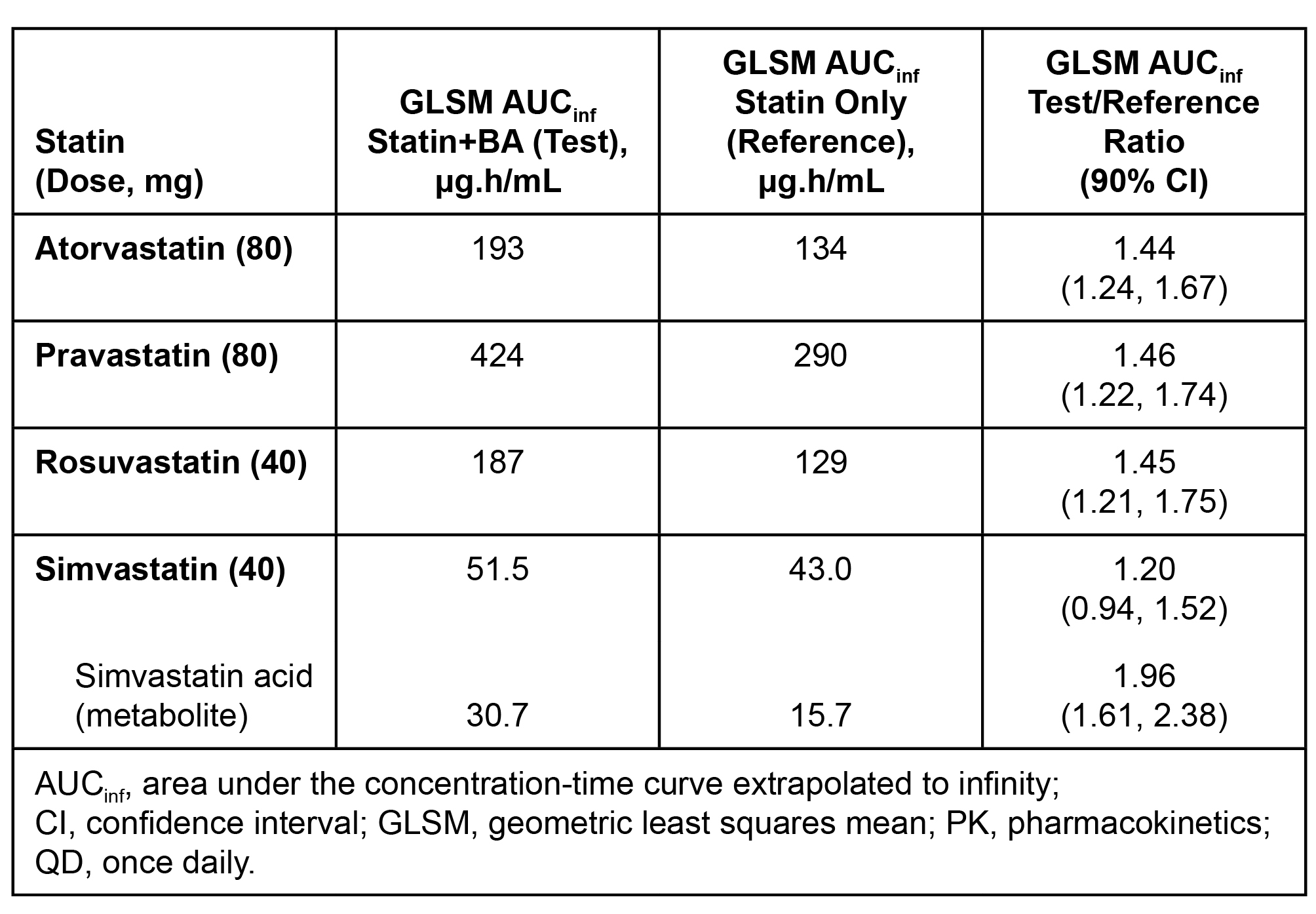
Results: Steady-state BA 180 mg was associated with mean AUC increases of < 1.5-fold (atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, and pravastatin) and 2-fold (metabolite simvastatin acid).
Conclusion: Steady-state BA 180 mg had moderate effects on statin PK (AUC increase < 1.5-fold) that were generally not considered clinically meaningful, except for simvastatin acid. A maximum simvastatin 20 mg dose is recommended with BA 180 mg QD.
Statistical Analysis of Single-Dose Statin PK With Steady-State Bempedoic Acid 180 mg QD.